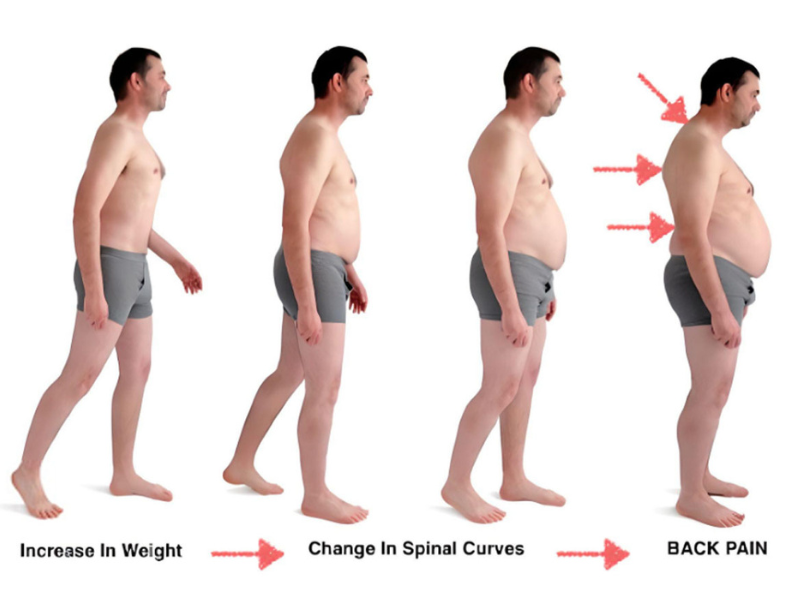
Unveiling the Mystery of Lower Back Pain
June 15, 2023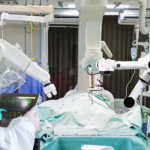
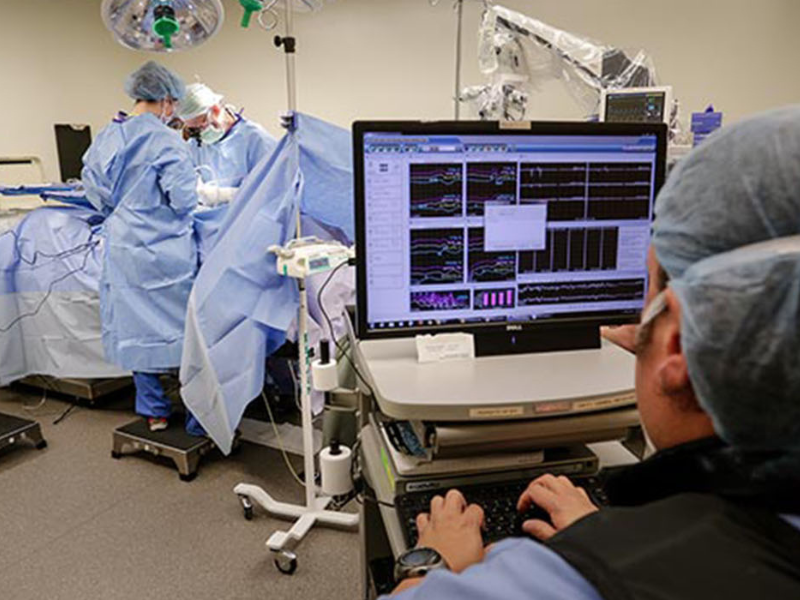
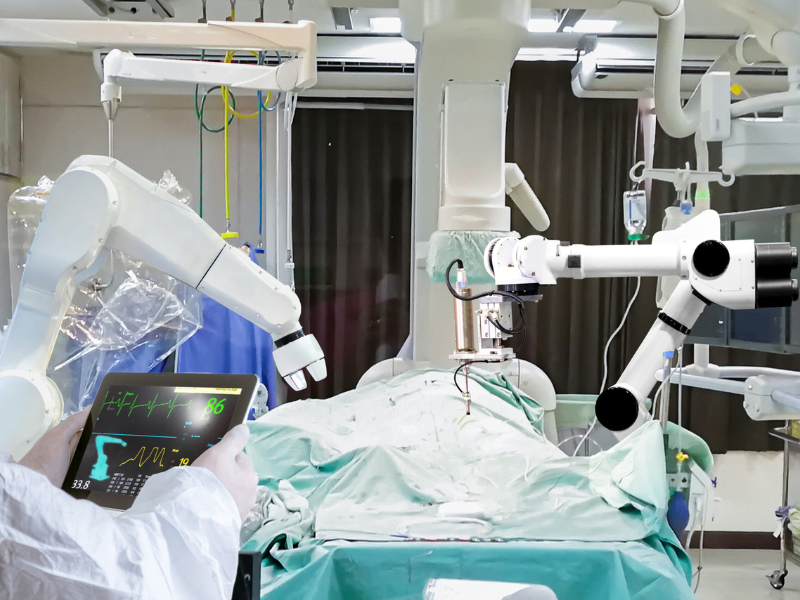
Revolutionizing Spinal Surgery: The Remarkable Benefits of Robotics
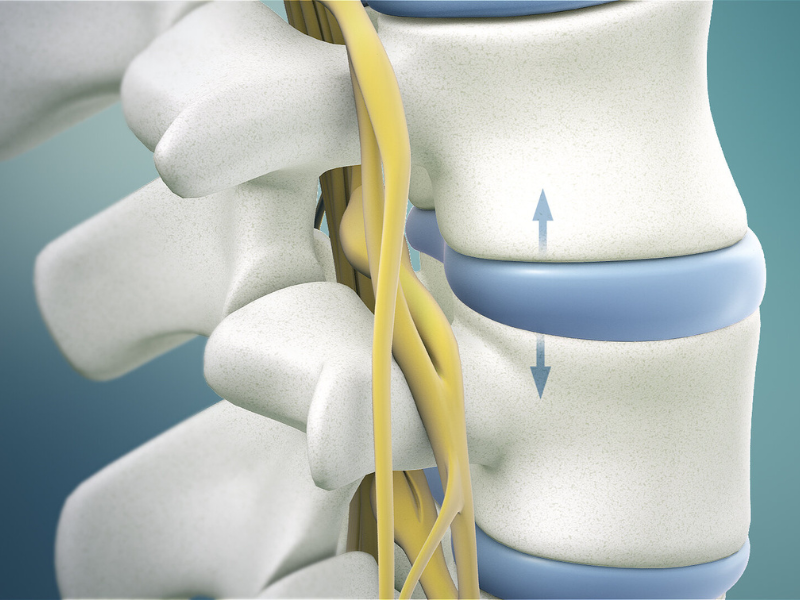
August 15, 2023Degenerative disc disease (DDD) is a common condition that affects the intervertebral discs of the spine. Despite its name, DDD is not technically a disease but rather a natural part of the aging process. This condition can cause pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility, significantly impacting an individual’s quality of life. In this blog post, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for degenerative disc disease, providing a comprehensive understanding of this prevalent spinal condition.
Causes of Degenerative Disc Disease:
Degenerative disc disease primarily occurs due to the natural wear and tear that happens to the spinal discs over time. The intervertebral discs act as shock absorbers between the vertebrae, providing cushioning and flexibility. With age, these discs gradually lose their water content, making them less flexible and more prone to damage. Other factors that can contribute to DDD include repetitive strain, injury, obesity, and genetic predisposition.
Symptoms of Degenerative Disc Disease:
The symptoms of degenerative disc disease can vary depending on the location and severity of the affected discs. Common signs and symptoms include:
- Chronic Back or Neck Pain: DDD often manifests as persistent pain in the affected area. The pain may worsen with certain activities or movements and may be accompanied by muscle spasms.
- Radiating Pain: When degenerated discs impinge on spinal nerves, it can result in radiating pain, tingling, or numbness. This pain can travel (radiate) down the arms or legs, depending on the location of the affected discs.
- Reduced Mobility: Stiffness, limited range of motion, and difficulty performing daily activities can be experienced due to the degenerative changes in the discs.
Treatment Options for Degenerative Disc Disease:
Non-Surgical Approaches:
- Physical Therapy: Targeted exercises, stretching, and core strengthening can help improve flexibility, relieve pain, and enhance overall spinal stability.
- Pain Management: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), muscle relaxants, and analgesics may be prescribed to manage pain and inflammation.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Maintaining a healthy weight, practicing good posture and avoiding activities that strain the spine can alleviate symptoms and slow down the progression of DDD.
Surgical Interventions:
- Discectomy: In cases where a herniated or damaged disc is causing severe pain or nerve compression, surgical removal of the affected disc (discectomy) may be necessary.
- Spinal Fusion: This procedure involves fusing adjacent vertebrae to provide stability and alleviate pain. It may be recommended when DDD leads to spinal instability or when other conservative treatments have failed.
Emerging Treatments:
- Regenerative Therapies: Innovative treatments, such as stem cell therapy or platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections, show promise in promoting disc healing and reducing symptoms in select cases. However, more research is needed to establish their long-term efficacy.
Degenerative disc disease is a common spinal condition that affects a significant number of people as they age. While it is an inevitable part of the aging process, there are several treatment options available to manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Non-surgical approaches, including physical therapy and lifestyle modifications, are often the first line of treatment. In more severe cases, surgical interventions such as discectomy or spinal fusion may be recommended. With advancements in medical research, regenerative therapies hold the potential to offer further options for the treatment of degenerative disc disease. If you are experiencing symptoms of DDD, consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate treatment plan for your specific situation.


1 Comment
Good https://is.gd/tpjNyL